TECHNOLOGY HELPING TO DEVELOP AN INNOVATIVE PROFESSIONAL PROFILE
Remembering that innovation can assist with developing new conditions, new points of view and diverse instructive and social modalities, the information society ought to recognize how innovation influences the data society, the correspondence society, and the system society.
Introduction
A portion of the inquiries raised concern the requirement for new preparing conditions that are as per the instructor’s profile; include issues, for example, who creates the substance?, by what method will these substance be transmitted and assessed?; and propose the age of systems for advancing collective and helpful work.
In light of these inquiries, activities ought to be recommended that empower instructors to turn out to be mechanically equipped and permit the clients of this guidance and preparing procedure to secure a lot of abilities, methods, mentalities and propensities that require the right utilization of innovative apparatuses and accommodate a fruitful educator preparing process.
On education policy and initial teacher training
The present information age process contains a blend of shared learning and cooperation that requires a fair mix including an intellectual segment, an enthusiastic part, and an enormous stockpile of social aptitudes.
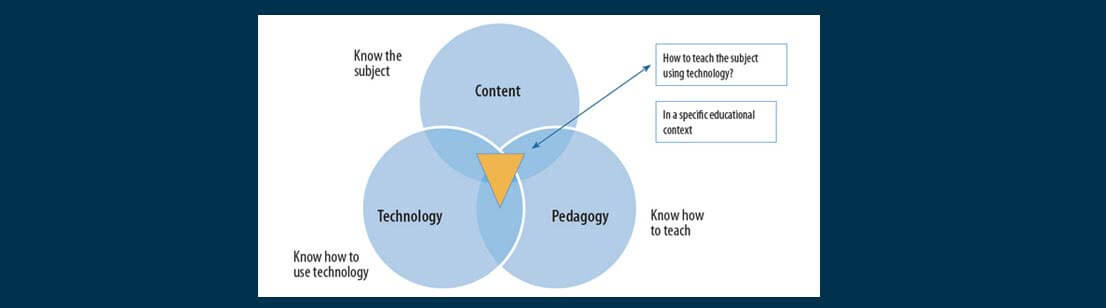
Remembering that data is progressively open gratitude to the approach of ICTs, an instructing profile that depends on the minor transmission of encouraging substance is currently inane. The instructor’s job is never again to give students data however to manage them through the way toward looking and treating data with the goal that they become liable for effectively and tentatively developing their own insight.
Essential Competences
Below are just some of the essential competences teachers need in order to exercise their profession in the twenty-first century:
- Subject competence
- Teaching competence
- The ability to combine theory and practice
- Cooperation and collaboration
- Quality assurance
- Mobility
- Leadership
- Continuous learning
On Change Management
We have to comprehend and acknowledge that the “map” of instructing and learning forms isn’t actually the genuine “domain” of the study hall or of every student. Above all else, educators ought to have an open (which isn’t to state guileless) disposition. They ought to be set up to “investigate” the potential outcomes gave by mechanical instruments to reestablishing their educating and learning situations, for example they ought to permit themselves to be astonished and ought not have any pre-decisions when meeting the difficulties presented by innovation.
Also, as opposed to working alone, educators should work in groups, imparting their classwork to different instructors. Online innovation upheld community work can help immensely right now.
Thirdly, instructors should archive what they do and share their advancements. We have amazing experts who advance each day yet who don’t record what they do.
Fourthly, we have to manage as a top priority and comprehend the unique circumstances and the “psychological maps” of our educators in regards to development and change. Change the executives has more to do with dread and feeling than with reasonable concerns.
Lastly, we need a dream of development that offers us the chance to investigation and commit errors without turning out to be “deadened” or stable. Gaining from botches empowers us to learn and to advance.
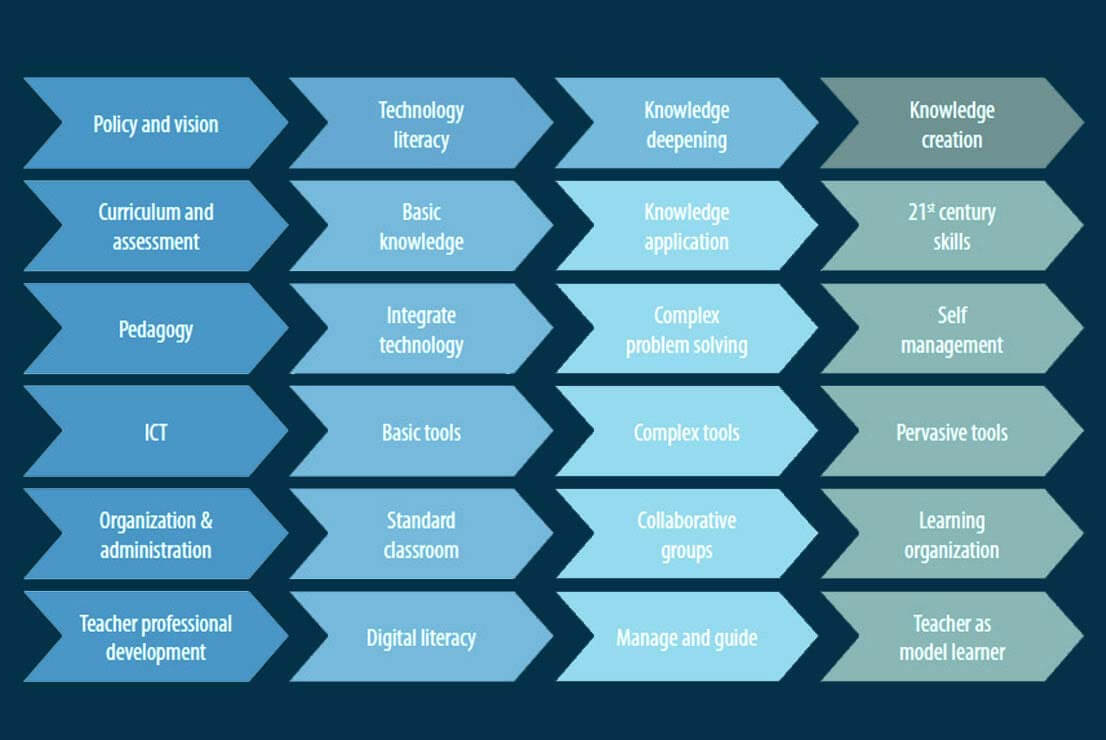
On teachers’ skills development
Various investigations have focused on the significance of creating aptitudes to guarantee that people partake in the information society of the twenty-first century (Ananiadou and Claro, 2009; Claro et al., 2012; Pedró, 2006; Sánchez, Salinas, and Harris, 2011). These abilities, as a rule named “of the twenty-first century” (Claro et al., 2012; Partnership for 21st Century Skills, 2014), go past practical aptitudes like realizing how to utilize a PC or distinctive programming. Despite the fact that there are various methodologies with respect to the idea of these abilities, it is generally concurred that they include more elevated level information that is connected to inventive exercises just as to advancement, correspondence and cooperation, data the executives, critical thinking, citizenship and the moral difficulties that have gotten basic in computerized situations (Ananiadou and Claro, 2009; Bennett, Maton, and Kervin, 2008; Claro et al., 2012; ISTE, 2014; Sánchez, Salinas, Contreras, and Meyer, 2011).
For understudies to build up these abilities, instructors must have the option to ace them and be fit for educating them. Studies on the information and practices educators need so as to encourage these abilities are steady with the significance given to instructors to make upgrades in the training frameworks (Barber and Mourshed, 2007; Darling-Hammond and Bransford, 2005; Twining, Raffaghelli, Albion, and Knezek, 2013).
Various nations and associations have created models planned for improving instructor execution. A few, including the ISTE Standards (once in the past the NETS) for Teachers1 and the UNESCO ICT Standards for Teachers (UNESCO 2011) join the information and practices expected to help build up understudies’ twenty-first century aptitudes.
